Critical Locations of Internal Bleeding
Even though any organ can be damaged and lead to internal bleeding, there are certain regions in the body that are considered most serious and require medical attention immediately.
- Intracranial hemorrhage (head)
- Hemopericardium (heart)
- Hemothorax (lungs)
- Center of the body where large blood vessels are located
Causes of Internal Bleeding
Internal bleeding often occurs after major physical injury, usually due to trauma. There are two main types of trauma that may lead to internal bleeding:
- Penetrating trauma
- Penetration of foreign object in the body, creating a hole in one or more blood vessels
- E.g. stab wounds, gunshot wounds, falling onto sharp objects
- Blunt trauma
- Collision of a body part with another strong force, usually at high speed
- Blood vessels inside the body are crushed or torn by blunt objects
- E.g. falls, physical assaults, car accidents
- Others
- Fractures
- Pregnancy
- Alcohol abuse
- Medication
Symptoms of Internal Bleeding
External bleeding is easier to identify because it is obvious from a cut, abrasion or laceration, the greater challenge is to detect internal bleeding. However,extensive external bleeding should be associated with internal bleeding, especially if due to penetrating trauma. In cases of severe internal bleeding, injury is typically obvious and serious. Symptoms will differ based on the type of trauma, amount of blood lost and the body region involved:
- Typically, inflammation and pain
- Light-headedness, dizziness and unconsciousness if there is severe blood loss
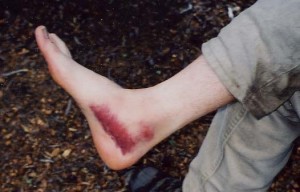
- Ecchymosis (deeply purple skin) if in the skin and soft tissues
- Swelling and stiffness often if in the limbs
- Blood in vomit or stools if in gastrointestinal tract
- Swelling and abdominal pain if in the liver or spleen
- Headache, confusion and unconsciousness if in the brain
First Aid for Internal Bleeding
If one is unsure, it is always better to assume to worst and treat
for internal bleeding. If possible, have someone call for an ambulance immediately. Give first aid while waiting for the ambulance.
- If possible, wear gloves in case external bleeding occurs.
- Check for airway, breathing and circulation. If necessary, initiate CPR.
- If he victim is conscious, advice the victim lie down and elevate the legs if possible.
- If the victim is unconscious and breathing and with no apparent head, neck or spinal injury, place the victim in recovery position.
- Cover the victim with a coat or blanket to avoid shock. However, if symptoms of shock are observed, treat for shock.
- Consistently check and monitor vital signs. Do not leave the victim alone at all times.
Internal bleeding is a medical emergency and giving first aid might just help save a life. Enrolling in first aid courses can help treat and manage victims of medical emergencies, especially those with bleeding, whether internally or externally, injuries.